At Glebe, computing is considered as a practical subject for the 21st century, in which invention and resourcefulness are encouraged. The ideas of computing are applied to understanding real-world systems and creating ambitious products. Each year group follows a sequence of learning each term which includes, safety, computer science information technology and digital literacy. Over the course of the year, children build upon prior knowledge taking this with them throughout their primary education. Computing at Glebe, therefore, provides a wealth of learning opportunities and transferrable skills that help children to understand how the world around them works. We encourage our staff to try to embed computing across the whole curriculum to make learning creative and accessible. We also believe that Online Safety is essential in ensuring children are safe in the digital world: We recognise that the best prevention for a lot of issues we currently see with technology/social media is through education. Online Safety is both embedded within lessons where appropriate and taught discreetly
Our Curriculum
Early Years Foundation Stage
For our very youngest learners in the foundation stage, we aim to give children a broad, play-based experience of computing in a range of contexts, including outdoor play. Computing is not just about computers. Early Years learning environments feature computing scenarios based on experience in the real world, such as in role play. Children gain confidence, control, and language skills through opportunities to ‘paint’ on the whiteboard or drive a remote-controlled toy.
Children in Key Stage 1 and 2 have access to class sets of ipads each week as well as VR headsets.
Key Stage 1
In the younger years children learn to use programmable toys for a purpose, ask questions when things don’t work and think of ways to improve their code using pictures and talk. Children then move on to creating simple programs through block coding and using a range of different software.
Key Stage 2
As children’s programming, reading and mathematical skills develop they move onto using more complex programs in Scratch, SketchPad and BeFunky. They also continue to develop their collaboration and co-operation working together using ClassNotebook. Teaching computing ensures our children develop a ’can do’ attitude to problem solving and logical thinking.
Our Aims
Key stage 1
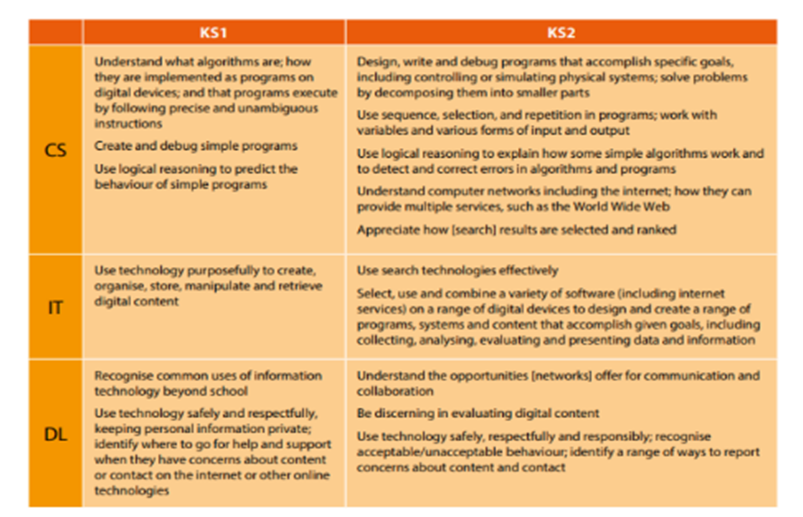
By the end of Key Stage 1 children should be able to:
- understand what algorithms are
- create and debug simple programs
- use logical reasoning to predict the behaviour of simple programs
- use technology purposefully to create, organise, store, manipulate and retrieve digital content
- recognise common uses of information technology beyond school
- use technology safely and respectfully
Key stage 2
- By the end of Key Stage 2 children should be able to:
- design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals
- use sequence, selection, and repetition in programs
- use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work
- understand computer networks including the internet
- use search technologies effectively
- select, use and combine a variety of software (including internet services) on a range of digital devices
- use technology safely, respectfully and responsibly; recognise acceptable/unacceptable behaviour; identify a range of ways to report concerns about content and contact.
Computing At Home
Barefoot (KS1 and KS2)
https://www.barefootcomputing.org/homelearning
Downloadable activities and games for children, links to live lessons and a guide for parents - includes cross-curricular lesson plans and resources that unpack computational thinking in a range of subjects.
Code Club (KS2)
https://projects.raspberrypi.org/en/codeclub
Projects and activities for home learning and a parent guide.
UK Safer Internet Centre (KS1 and KS2)
https://www.saferinternet.org.uk/advice-centre/young-people/resources-3-11s
Online safety resources aimed at 3 -11 year olds.
STEM Learning e-Library (KS1 and KS2)
https://www.stem.org.uk/primary-computing-resources
An online resource bank, which links to resources on external websites. The site features a live chat function offering support from subject experts. New home learning resources are being developed.
Raspberry Pi Foundation – Digital Making at Home (KS2)
https://www.raspberrypi.org/at-home/
Join the weekly code-along using open projects based on a weekly theme, with different levels available for all abilities, allowing you to be open-ended with opportunities for making and creativity.
Computing at School - Home Learning (KS1 and KS2)
https://www.computingatschool.org.uk/homelearning
Information and links to a range of at home computing activities
Thinkfun – All ages
http://info.thinkfun.com/stem-education/6-unplugged-coding-activities-for-hour-of-code
Unplugged activities for children to learn the basics about algorithms without a computer.
Things to do
Computing (coding) is important for children as it will help improve their mathematics and writing skills, it will give them valuable life skills, which will be used eventually in the workplace. Develop your child’s skill by start learning the basics of coding; you do not even need a computer! Problem solving, thinking creatively, and it helps them to develop resilience.
Pupil Voice
What have you enjoyed about your topics?
“I like Tinkercad it allows you to make anything you want” (Year 6)
“I enjoyed seeing what I have made” (Year 5)
“I like drawing pictures and making them move” (Year 3)
What skills have you learnt?
“How to code” (Year 5)
“How to move characters, I’ve mastered that now” (Year 4)
“Using the mouse better” (Year 2)
Is there anything else you would like to learn?
“Make your own flipbook” (Year 3)
“How to do the tricky questions” (Year 5)
Pupils show a really positive attitude towards computing and are enjoying their lessons. Pupils are starting to be more detailed in the way they explain their work and the programmes they use on the computer.
Further information regarding E-Safety can be found here

















